Molecular Biology S1 Module 2: DNA and Replication
- 18 שאלות
- 1 תגובות
- 0% הושלמו
- equalizer סטטיסטיקות
- share שתף
מנהלים:

Discuss, Learn and be Happy דיון בשאלות
help
brightness_4
brightness_7
format_textdirection_r_to_l
format_textdirection_l_to_r
During DNA polymerase activity, the entry of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates to the enzyme active site
1
| done | ||
מיין לפי
Some bases in DNA are occasionally methylated, typically C in eukaryotes and A in prokaryotes. This provides an additional ‘code’ to the information stored in DNA. How is this code maintained during DNA replication?
1
| done | ||
מיין לפי
Which of the following activities is/are never associated with a DNA polymerase?
1
| done | ||
| done | ||
| sentiment_very_satisfied | ||
מיין לפי
Is there a naturally occurring DNA polymerase that does not require a template? YES OR NO
1
| done | ||
This question is just nasty - but it does make you think.
The enzyme TdT (Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase) catalyses the addition of nucleotides onto 3' DNA ends without any template. It is therefore considered a DNA polymerase. It is found largely in B- and T-cells. Remember it as you learn about lymphocytes in Immunology.
Then there is the whole issue of Translesional DNA polymerases. It's a bit of a stretch to consider the contiguous strand sitting under the active site a 'template' if there is no base there.
The correct answer is: Yes.
מיין לפי
Given the reactants shown, which of the images underneath is the most likely reaction product?

1
| done | ||
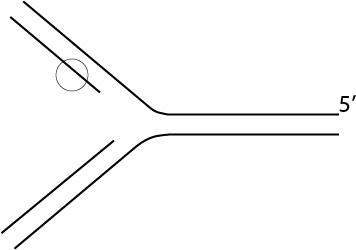
(USMLoid) During genome replication, hydrogen-bonding between the two DNA strands is broken and the strands separated from each other. Which of the following is responsible?
1
| done | ||
מיין לפי
The picture shown is an electron micrograph of a naturally occurring DNA structure. It is most likely:
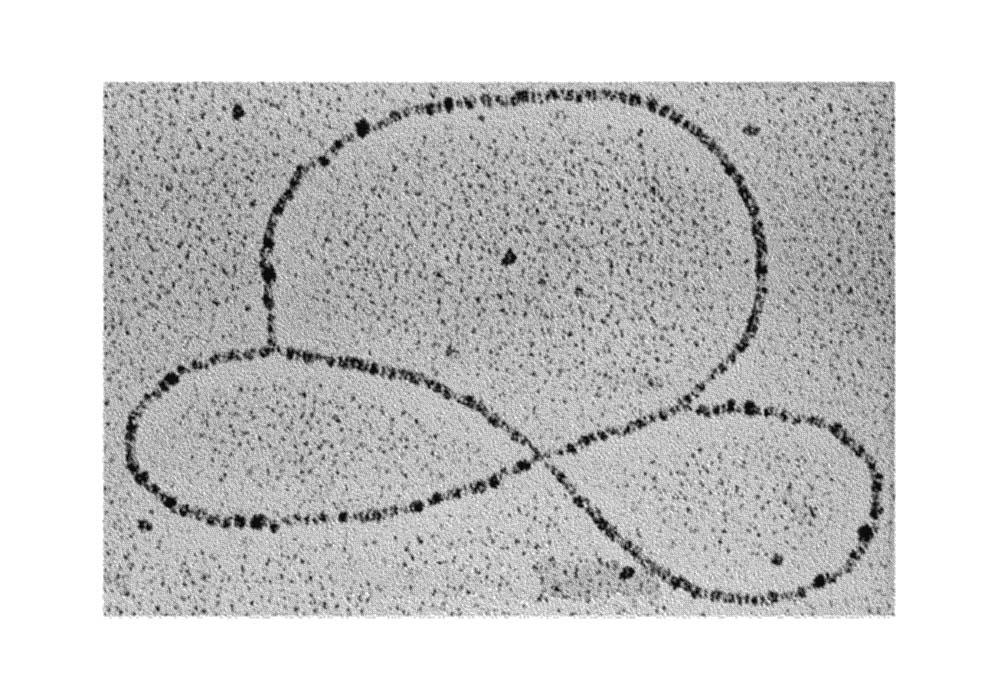
1
מיין לפי
(USMLoid) In human chromosomes, which of the following elements or properties works to ensure that information is not lost from the chromosome ends during cell proliferation?
1
| done | ||
מיין לפי